Matilal Nehru Road, Opposite Prag Continental Hotal, Pan Bazar, 781001, Guwahati
ECG Machine
ECG Machine for Rent
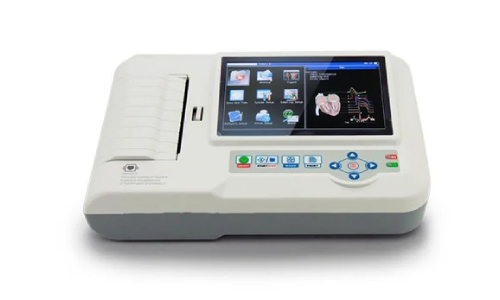
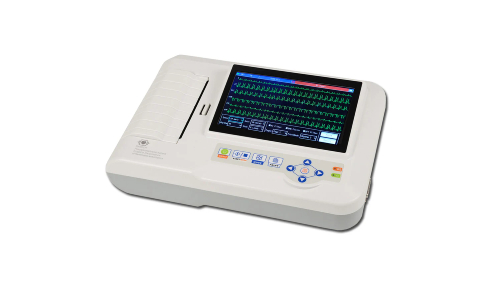
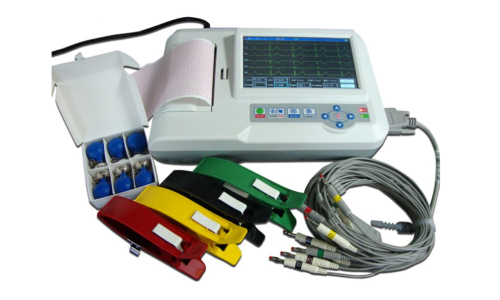



An ECG (electrocardiogram) machine is a medical device used to record the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. This test is crucial for diagnosing various heart conditions, including arrhythmias, myocardial infarctions, and other cardiac abnormalities.
Feature
- Electrodes: Typically, an ECG machine uses 10 electrodes attached to the skin of the chest, arms, and legs to detect the heart's electrical activity.
- Leads: The machine produces a graphic representation of the heart's activity in multiple leads (usually 12), each offering a different view of the heart.
- Display and Printout: Most machines provide a digital display of the heart's electrical activity and print out the results on graph paper.
- Portable and Stationary: Available in both portable models for field use and larger, stationary units for hospital settings.
- Storage and Transmission: Modern ECG machines often have memory storage for patient data and the capability to transmit data to electronic health records (EHR) systems.
- Diagnostic Tool: Essential for diagnosing heart conditions such as arrhythmias, ischemia, and myocardial infarction.
- Non-Invasive: A safe and non-invasive procedure with no risk to the patient.
Copyright © All Surgical. Designed By Web Infotech